Executive Summary
Operating rooms (ORs) play a pivotal role in healthcare organizations, and staffing is essential for delivering patient care, achieving surgeon satisfaction, and maintaining financial sustainability. However, staffing is also one of the greatest expenses for hospitals, and inefficient usage can strain already tight margins and harm overall profitability. Traditional staffing schedules, combined with dynamic OR needs can lead to overstaffing, productivity variances, underutilization of resources, and missed financial targets. Surgeon preferences, unpredictable caseloads, and inefficient scheduling can further exacerbate these problems.
As an integrated ecosystem, all chief decision-makers and stakeholders in the hospital— from the c-suite to physician and nursing leaders and surgeons—can be negatively affected by these challenges. These individuals also hold power for positive influence and change. The key is adopting innovative solutions that optimize staffing efficiency while meeting patient care demands and aligning with financial objectives. These solutions include leveraging advanced technologies, redefining staffing financial metrics, and enhancing surgeon engagement.
PROBLEM
Traditional Staffing Schedules are Outdated
OR staffing presents a complex problem that stems from the intersection of clinical, operational, and financial factors. At the core of these challenges lies traditional staffing schedules that adhere to rigid timeframes and fail to accommodate the dynamic nature of surgical caseloads. Hospital administrators and OR managers often struggle to match staffing levels with fluctuating demand. The outcome is usually overstaffing or understaffing throughout the day.
The financial implications of poor staffing decisions pose significant concerns for healthcare organizations. While finance teams provide staffing targets based on case minutes, these metrics do not adequately account for staff downtime during periods of inactivity in the OR. As a result, hospitals may exceed budgetary constraints due to inefficiencies in resource utilization, such as prolonged room turnover times and idle staff hours.
Surgeon preferences also contribute to staffing challenges, as clinicians request additional resources or specialized support personnel to facilitate the needs of their specific surgical procedures. While accommodating surgeon preferences is important for optimizing patient care, it can further complicate staffing decisions and intensify productivity variances among surgical teams.
SOLUTION
Adopt a Multifaceted Staffing Approach
To address OR staffing challenges, we advise healthcare organizations rethink their staffing decision-making process by embracing technological innovation, process optimization, and stakeholder collaboration.
Key strategies include:
1 | Implement advanced staffing optimization tools: Healthcare facilities should leverage cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning to analyze historical data, predict surgical caseloads, and optimize staffing levels in real time. Tools such as MerlinTM Periop Nurse Staffing enable proactive decision-making and facilitate the dynamic allocation of resources based on true demand fluctuations.
2 | Redefine financial metrics for staffing targets: Hospital finance teams should collaborate with OR management to develop more comprehensive metrics for staffing targets that incorporate factors such as room utilization, turnover times, and surgeon productivity. By aligning financial incentives with operational goals, healthcare organizations can optimize resource allocation while maintaining fiscal responsibility.
3 | Enhance communication and collaboration with surgeons: OR leaders should foster open communication channels with surgeons to understand their preferences, anticipate resource needs, and proactively address concerns. By engaging clinicians in the staffing decision-making process, hospitals can foster a culture of collaboration and accountability that enhances overall efficiency and productivity.
Practical Steps for Implementation
Achieving optimal OR staffing requires a systematic approach. Implementation steps include:
Step 1: Assess the Current State: Conduct a comprehensive assessment of existing staffing practices, operational workflows, and financial metrics to identify areas of inefficiency and opportunities for improvement. Determine the number of resources required for each day, including direct staff (nurses, surgical technologists), variable staff (RNFAs, PAs), and indirect staff (schedulers, assistants, managers, educators, EVS personnel, extra scrub team members).
Step 2: Identify Key Stakeholders: Engage key stakeholders, including OR managers, surgeons, and finance personnel, to gain buy-in and support for staffing optimization initiatives. Engage surgeons in discussions about resource requests. Balance surgeons’ needs with overall productivity goals.
Step 3: Invest in Technology: Advanced staffing optimization tools and software solutions that harness data analytics, predictive modeling, and machine learning algorithms drive optimized resource allocation and improved operational efficiency. To address challenges with OR staffing, healthcare organizations can leverage innovative solutions such as Merlin Periop Nurse Staffing. This proprietary staffing tool is designed to enhance nurse leaders’ ability to determine appropriate staffing levels based on the day of the week and time of day. Merlin Periop Nurse Staffing utilizes advanced algorithms and predictive analytics to review historical data, forecast demand, and create optimized staffing schedules. By incorporating factors such as surgical caseloads, room utilization, and surgeon preferences, Merlin Periop Nurse Staffing empowers nurse leaders to make informed staffing decisions that align with operational goals and financial objectives.
RESULTS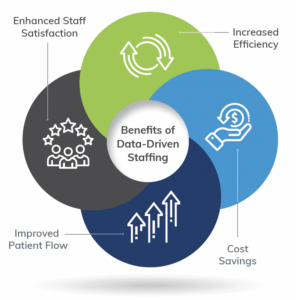
Staffing When and Where it is Needed
Leveraging technology such as Merlin Periop Nurse Staffing and adopting a data-driven approach offer a myriad of benefits for healthcare organizations. These include increased efficiency, substantial cost savings, improved patient flow, and significantly enhanced staff satisfaction.
With Merlin Periop Nurse Staffing’s dynamic staffing optimization capabilities, hospitals can ensure optimal resource allocation, minimize overstaffing, and reduce overtime costs. Moreover, the predictability of schedules provided by Merlin Periop Nurse Staffing contributes to higher staff satisfaction, enabling employees to plan their work-life balance more effectively. Collaborating with surgeons and integrating leadership input from staff further enhances the effectiveness of these solutions. By embracing innovation and implementing data-driven strategies, hospitals can overcome staffing challenges and achieve optimal patient outcomes, marking a significant improvement over existing industry practices.
Conclusion
Staffing remains a prominent hospital challenge. To use this resource wisely, hospital leaders must embrace data-driven strategies in their decision-making processes. Predictive analytics and optimized shift lengths can boost productivity. More effective use of staff can help control costs, improve schedule dependability, and enhance overall resource allocation. By embracing a culture of innovation and collaboration, healthcare organizations can move past the challenges associated with ineffective OR staffing to achieve sustainable improvements in OR efficiency, patient care throughput, and staff retention and satisfaction.
10 Applications of Merlin Periop Nurse Staffing
1 | Dynamic Staffing Optimization: Dynamically adjusts staffing levels based on OR utilization, ensuring optimal resource allocation and minimizing overstaffing or understaffing.
2 | Flexible Scheduling: Enables flexible scheduling based on changes in the block schedule, new surgeon additions, or departures, allowing nurse leaders to adapt staffing plans seamlessly.
3 | Financial Integration: Integrates with financial data to provide accurate staffing targets that account for staff downtime and maximize productivity within budgetary constraints.
4 | Surgeon Preference Management: Evaluate additional resource requests to optimize overall staffing efficiency.
5 | Predictive Modeling: Provide a >95% confidence level for room utilization predictions. This software considers historical patterns and helps forecast the number of ORs needed at specific times.
6 | Shift Length Optimization: Use formulas to determine appropriate shift lengths based on predicted OR demand. Consider factors such as case complexity, room turnover times, and surgeon preferences.
7 | Cost Analysis: Attach dollar amounts to predicted staffing needs. Compare these costs with existing staffing budgets to assess potential savings.
8 | Dynamic Staffing Adjustments: Factor in productivity elements such as downtime, late starts, and room turnover times. Adjust staffing levels accordingly.
9 | Incorporating Productivity Factors: Consider financial metrics for staffing targets that align with operational objectives, such as room utilization, turnover times, and surgeon productivity.
10 | Room Utilization Patterns: Identify when ORs are typically active by analyzing historical data. Consider time of day and day of the week.