Introduction
As hospital leaders navigate the complexities of optimizing surgical services, a significant challenge lies in balancing surgeon access with operational efficiency. Flip rooms—a process where surgeons use two operating rooms concurrently—can be a solution to boost surgeon productivity. However, when not implemented effectively, flip rooms can create inefficiencies that harm both the bottom line and overall operational performance.
This white paper explores how hospitals can leverage data-driven insights to optimize flip room utilization, improve block scheduling, and increase efficiency and productivity. With the right tools and strategies, hospitals can create a decision-making process that benefits both surgeons and operational leaders.
Problem
Inefficiencies in Flip Room Utilization
The initial appeal of a flip room is simple: Surgeons can perform more cases in a single day by moving from one operating room (OR) to the next without turnaround time or other delays. This reduces downtime between patients for the surgeon and ideally creates higher volume. However, complications arise when flip rooms are not properly allocated or utilized, creating the opposite effect by decreasing OR productivity.
In many cases, surgeons may request flip rooms without any clear structure or standardized guidelines for their use. For instance, a hospital in Illinois granted flip rooms to surgeons without performance-based criteria. This resulted in surgical cases being wastefully distributed, with some surgeons performing only three or four cases per day across two rooms, when flip rooms should yield six to eight cases daily.
With the cost of running an OR averaging between $50 to $85 per minute, under-used flip rooms increase the overall cost of running the OR. Flip rooms left idle, with additional surgical teams and anesthesia staff on stand-by, waste valuable time and revenue for hospitals, while also contributing to lower overall productivity for staff.
Solution
Data-Driven Block Scheduling and Flip Room Allocation
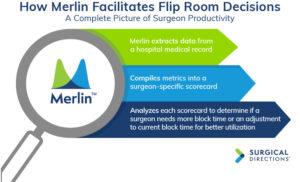
To resolve these inefficiencies, Surgical Directions implemented a structured, data-driven approach to block scheduling and flip room allocation. By using our proprietary software MerlinTM, hospitals can gain access to critical insights regarding surgeon productivity, case volume, block utilization, and turnaround times. These data points form the foundation for effective decision-making when assigning flip rooms to ensure OR resources are used optimally and fairly.
Establishing Criteria for Flip Rooms
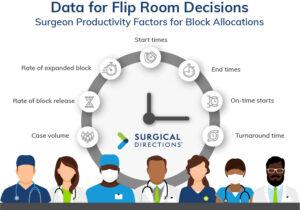
The first step is defining clear, data-backed criteria for flip room allocation. To maximize efficiency, Surgical Directions recommends the following guidelines for determining which surgeons qualify for a flip room:
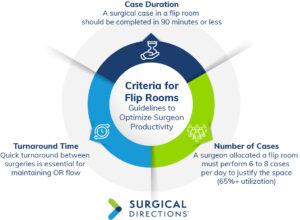
- Case Duration: Surgeons should perform cases that last no longer than 90 minutes. Longer cases reduce the productivity of the second operating room, leading to significant downtime and rendering the flip room inefficient.
- Number of Cases: Surgeons must be capable of performing six to eight cases (65% or higher utilization) per day to justify requesting a flip room.
- Turnaround Time: Quick turnaround times between surgeries in each room are essential for maintaining OR flow. Data from Merlin helps monitor turnaround efficiency and identify potential bottlenecks.
These parameters were successfully applied at the above-mentioned hospital in Illinois, where flip room usage was standardized and surgeon efficiency dramatically improved. The key was leveraging metrics to inform decisions, ensuring surgeons met the required benchmarks for requiring a stand-by OR before assigning one.
Continuous Monitoring and Governance
Merlin plays a crucial role in continuously monitoring OR performance. The software provides real-time information on individual surgeon performance, including block utilization, case volume, and on-time starts, extracted from a hospital’s medical record. This creates scorecards with a complete picture of each surgeon’s productivity metrics, empowering hospital leadership.
Surgical Directions recommends a collaborative approach, where administrators, OR directors, surgical executive committees, surgeons, and anesthesia leads work together to evaluate block schedules on a regular basis. This prevents stagnation in the OR and ensures modifications can be made swiftly to accommodate variation in surgeon availability, case load, and resource needs.
By working with a structured governance committee and regularly reviewing block and flip room performance, hospitals can increase fairness and efficiency. This continuous review also facilities growth opportunities within the surgical department, enabling surgeons to take on more cases based on effectiveness versus seniority without overloading OR resources.
Using Merlin, Surgical Directions’ proprietary software, an OR director or block subcommittee
can make better decisions about flip room allocation and have fact-based discussions with surgeons.
Results
Improved OR Efficiency and Surgeon Satisfaction
Hospitals that have implemented Surgical Directions’ data-driven solutions to flip room management have seen significant improvements in both OR optimization and surgeon satisfaction. At the community hospital in Illinois, the white space—or idle time—in the OR was reduced dramatically with better flip room governance. This resulted in more predictable end times for surgical staff and surgeons.
Key results include:
- Increased Case Volume: By allocating flip rooms to surgeons who met the necessary performance criteria, the hospital increased the number of cases completed each day. Surgeons who previously performed only four cases in a single room were now completing up to seven cases using a flip room, without incurring overtime costs.
- Reduction in Overtime Expenses: With improved scheduling and better resource allocation, overtime expenses were reduced significantly. OR staff and anesthesia providers experienced fewer delays, leading to more consistent workdays and higher overall job satisfaction.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: The data from Merlin and regular governance meetings enabled the hospital to identify and address inefficiencies in real time. As a result, OR downtime was minimized, and anesthesia and nursing teams were better utilized, leading to an overall increase in hospital productivity.
- Optimized Anesthesia Staffing: In addition to improving surgeon satisfaction, the new scheduling system allowed anesthesia teams to plan their day more effectively. By reducing downtime between cases, anesthesia providers worked more efficiently, further contributing to cost savings for the hospital.

Conclusion
Optimizing flip room utilization requires a combination of data-driven decision-making, clear performance criteria, and a collaborative approach to governance. By leveraging Merlin and implementing structured scheduling practices, hospitals can reduce OR inefficiencies, increase case volumes, and improve overall surgeon and staff satisfaction.
The success of Surgical Directions’ approach at hospitals across the country demonstrates the power of data in transforming surgical services. Hospitals that embrace these solutions will not only see financial benefits but also create a more positive and efficient environment for both patients and healthcare providers.